Blood sugar test
Random blood sugar; Blood sugar level; Fasting blood sugar; Glucose test; Diabetic screening - blood sugar test; Diabetes - blood sugar testA blood sugar test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a sample of your blood. Glucose is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, including brain cells. Glucose is a building block for carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are found in fruit, cereal, bread, pasta, and rice. Carbohydrates are quickly turned into glucose in your body. ...
The Basics
Tests for diabetic screening - blood sugar test
A Closer Look
- Diabetes - type 2 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes - type 1 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- High blood pressure - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes (Alternative Medicine)
- Stroke - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Coronary artery disease - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Heart attack and acute coronary syndrome - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Peripheral artery disease and intermittent claudication - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Cholesterol - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Urinary tract infection - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Self Care
HbA1c - Animation
HbA1c
Animation
Type 1 diabetes - Animation
Type 1 diabetes
Animation
Colon cancer screening - Animation
Colon cancer screening
Animation
Newborn screening testing
Blood is routinely drawn from newborn infants for testing. Blood is obtained by a heel stick and collected on a special blotter paper. Routine testing usually includes phenylketonuria, thyroid function, hemoglobin S (sickle cell disease), and may test for other disorders. Newborn screening programs vary from state to state. Testing can be tailored to the local population, determining what routine testing should be done.
Newborn screening testing
illustration
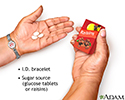
Diabetic emergency supplies
An individual with diabetes should wear or carry I. D. information (such as an alert bracelet) that emergency medical staff can find. A sugar source, such as glucose tablets or raisins should be carried in case blood sugar levels become too low.
Diabetic emergency supplies
illustration
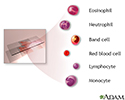
Complete blood count - series
Presentation
HbA1c - Animation
HbA1c
Animation
Type 1 diabetes - Animation
Type 1 diabetes
Animation
Colon cancer screening - Animation
Colon cancer screening
Animation
Newborn screening testing
Blood is routinely drawn from newborn infants for testing. Blood is obtained by a heel stick and collected on a special blotter paper. Routine testing usually includes phenylketonuria, thyroid function, hemoglobin S (sickle cell disease), and may test for other disorders. Newborn screening programs vary from state to state. Testing can be tailored to the local population, determining what routine testing should be done.
Newborn screening testing
illustration
Diabetic emergency supplies
An individual with diabetes should wear or carry I. D. information (such as an alert bracelet) that emergency medical staff can find. A sugar source, such as glucose tablets or raisins should be carried in case blood sugar levels become too low.
Diabetic emergency supplies
illustration
Complete blood count - series
Presentation
Blood sugar test
Random blood sugar; Blood sugar level; Fasting blood sugar; Glucose test; Diabetic screening - blood sugar test; Diabetes - blood sugar testA blood sugar test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a sample of your blood. Glucose is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, including brain cells. Glucose is a building block for carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are found in fruit, cereal, bread, pasta, and rice. Carbohydrates are quickly turned into glucose in your body. ...
The Basics
Tests for diabetic screening - blood sugar test
A Closer Look
- Diabetes - type 2 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes - type 1 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- High blood pressure - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes (Alternative Medicine)
- Stroke - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Coronary artery disease - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Heart attack and acute coronary syndrome - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Peripheral artery disease and intermittent claudication - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Cholesterol - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Urinary tract infection - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Self Care
Blood sugar test
Random blood sugar; Blood sugar level; Fasting blood sugar; Glucose test; Diabetic screening - blood sugar test; Diabetes - blood sugar testA blood sugar test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a sample of your blood. Glucose is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, including brain cells. Glucose is a building block for carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are found in fruit, cereal, bread, pasta, and rice. Carbohydrates are quickly turned into glucose in your body. ...
The Basics
Tests for diabetic screening - blood sugar test
A Closer Look
- Diabetes - type 2 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes - type 1 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- High blood pressure - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes (Alternative Medicine)
- Stroke - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Coronary artery disease - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Heart attack and acute coronary syndrome - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Peripheral artery disease and intermittent claudication - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Cholesterol - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Urinary tract infection - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Self Care
Review Date: 1/10/2025
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.